You must have seen lots of job listings for "UX/UI designer" and maybe thought they were the same thing, or wondered if there's a difference between ui and ux design? People often use User Experience (UX) and User Interface (UI) interchangeably, but they describe two different areas. One is about how things look, while the other is about how things work. If you're involved in creating a user-friendly digital experience, it's crucial to understand the main difference between UI vs UX.
UI vs UX Design: Key Differences
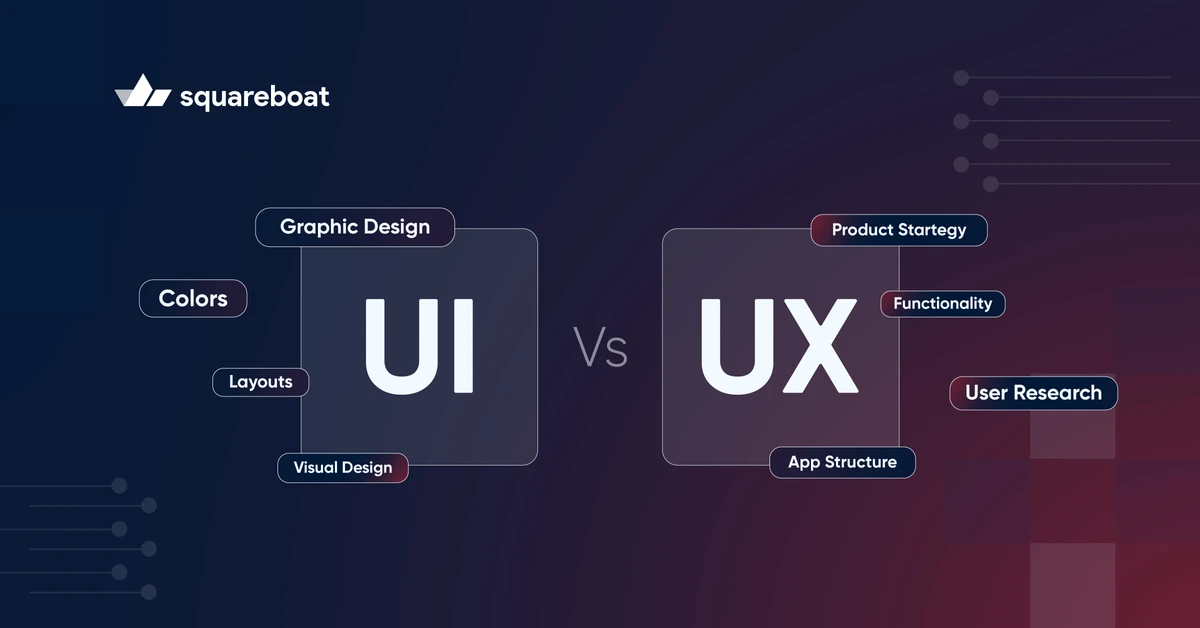
Although UI and UX work together, they focus on different parts of a digital product. In a nutshell, UI acts as the product's skin—the visual layer you interact with—while UX serves as the soul—the overall feeling you get when using it. Let's break down UI vs UX:
| Aspect | UI (User Interface) | UX (User Experience) |
| Definition | Involves creating the visual layout and interactive elements of a product | Focuses on enhancing the user's journey and satisfaction while interacting with the product |
| Goal | The main goal is to make the interface visually appealing and intuitive | The main goal is to improve usability, accessibility, and overall satisfaction |
| Core Components | Focuses on components like Buttons, icons, typography, color schemes, animations, and layouts | Focuses on components like User research, wireframes, prototypes, usability testing, and user personas |
| Design Focus | Focuses on looks, aesthetic appeal, and interaction elements of a product | Focuses on feel, usability, user flow, and ease of navigation aspects of a product |
| Main Tools | Most widely used tools are Sketch, Figma, Adobe XD, Photoshop, Illustrator | Wireframing tools (Balsamiq), prototyping tools (InVision), user testing platforms (Hotjar), research tools (Google Analytics) |
| Output | Expected outputs are high-fidelity visual designs, mockups, and interactive prototypes | Expected outputs are low-fidelity wireframes, user journey maps, usability reports, and feedback documentation |
| Primary Skills | Skills required are graphic design, color theory, typography, and visual hierarchy | Skills required are user research, psychology, problem-solving, and usability testing |
| Visual Appeal | High priority, as it influences the first impression | Low priority, as the focus is on functionality and usability |
| User Interaction | Focus on how users interact with visual elements (buttons, forms, icons) | Focus on how users feel and navigate through the product |
| Scope of Work | Designing the product’s appearance, creating responsive layouts, and maintaining brand consistency | Designing the user journey, testing usability, identifying pain points, and optimizing user satisfaction |
What is UI Design?
User Interface design shapes how a digital product looks and feels. It is the art of creating visually appealing and interactive layouts that make user interactions intuitive. From buttons to icons, colors to typography—UI gives a product its unique character. It ensures users find the design attractive and easy to use.
What does a UI Designer do: Role and Responsibilities
Being a UI Designer is like being a visual storyteller. This job involves more than just creating attractive designs, but also ensures users can navigate the interface without any discontinuity. Here’s what a UI Designer typically does:
- Visual Design: Creating attractive and easy-to-use visual elements. This involves picking colors, fonts, and icons that match the brand character while also making the interface look aesthetically pleasing.
- Interactive Design: Designing elements that respond to user actions, like buttons and sliders. The aim is to make interactions smooth and interesting to help users navigate the product without effort.
- Brand Consistency: Making sure the product's visual identity matches the brand's voice. Staying consistent helps build brand recognition and user trust.
- Prototyping: Building interactive models to show how the final product will appear and function. This step helps spot potential design problems early on.
- Teamwork: UI designers join forces with UX designers, developers, and stakeholders. This ensures that the look and feel go hand in hand with the user experience and meet tech specs.
- User Feedback: Getting input on visuals and how things work. Tweaking the design based on what we learn helps make sure the product hits the mark for users.
UI Designers connect aesthetics with practicality. Their efforts impact how happy users are, what people think of the brand, and how well the product does overall.
What is UX Design?
User Experience design focuses on how a product's functionality feels when a user uses it. It's not just about looks, but also how easy it is to navigate and interact with. UX design aims to create products that are easy, fun, and enjoyable to use. It involves learning what users want, finding their pain points, and coming up with answers that seem natural and intuitive.
What does a UX Designer do: Role and Responsibilities
A UX designer has an essential role in making products easy to use and fun. They aim to create meaningful and satisfying experiences for users. Let’s look at the key responsibilities of a UX designer:
- User Research: UX designers begin by getting to understand their target users. They talk to people, send out surveys, and watch how people use products to gather insights. This research helps them figure out what users need, like, and pain points are.
- Information Architecture: UX designers organize content in a way that makes sense to users. They lay out information so people can find their way around without difficulty. A well-organized setup cuts down on confusion and makes for a better user experience.
- Wireframing and Prototyping: UX designers sketch out wireframes and build prototypes to map the user's journey. Wireframes are basic layouts that show where stuff will go. Prototypes are hands-on versions that give a taste of the end product.
- Usability Testing: UX designers put their designs to the test with actual users to uncover any problems. They watch how people use the product and make it better based on what they learn. This step makes sure the product is easy to use and gets the job done.
- Interaction Design: They focus on how people use the product. This means creating how buttons work, how pages change, and how moving parts make it easier to use. Smooth interactions lead to a pleasant user experience.
- Visual Consistency: UX designers make sure all the visual parts match the overall look. They keep colors, fonts, and layouts the same throughout, which makes the product look good and easy to understand.
- Working Together with Teams: UX designers team up with UI designers, developers, and stakeholders. This teamwork makes sure the end product meets what users want and what the business needs.
UX designers have a big influence on how people perceive a product. When they focus on making things easy to use and keeping users happy, they help create products that people enjoy using. Their work affects how many users stick around, stay loyal to the brand, and how well the product does overall. A good user experience doesn't just meet what users expect - it leaves a positive lasting impression.
UX and UI Design: How Do They Work Together?
UI and UX complement each other and are crucial to creating successful digital products. While UI focuses on the product’s appearance, UX is about how users feel when interacting with it. Integrating these two ensures a seamless and visually appealing experience.
Here’s how they work together:
- Collaboration: UI and UX designers work together to make things look good and work well. A pretty interface that's tough to use doesn't help, and an easy-to-use interface that looks boring won't keep users interested.
- Consistency: A steady visual style led by UI design needs to match the easy navigation set up by UX research.
- User Testing: Both designers participate in usability testing. While UX designers focus on the flow, UI designers observe how users interact with visual elements.
- Feedback Loop: UX testing often shows where UI needs to change. Regular teamwork makes sure things get better without messing up how good it look.
- Adaptability: Both UI and UX need to change based on what users say and what's new. UI designer changes can make things more engaging, while UX designer changes can make things easier to use.
When UI and UX designers team up, they create products that are not just visually appealing but also functional. This teamwork makes sure users know how to use a product and have fun doing it. The balance of aesthetics and usability turns ideas into digital products that succeed.
Conclusion
UI and UX may seem like two sides of the same coin, but they play different roles in product design. In simple words, UI focuses on visual charm, while UX makes sure everything runs smoothly and is enjoyable. It's not about picking one over the other, but blending both to make a product that looks awesome and works even better. When UI and UX join forces, users get something that's pretty and works well—a perfect match!